VERBO TO-BE
|
forma afirmativa
|
forma negativa
|
forma interrogativa
|
| I am (I'm) |
I am not (I'm not) |
am I? |
| soy, estoy |
no soy, no estoy |
¿soy yo?, ¿estoy yo? |
| you are (you're) |
you are not (you're not) |
are you? |
| eres, estás |
no eres, no estás |
¿eres tú?, ¿estás tú? |
| he is (he's) |
he is not (he's not) |
is he? |
| él es, está |
él no es, no está |
¿es él?, ¿está él? |
| we are (we're) |
we are not (we're not) |
are we? |
| somos, estamos |
no somos, no estamos |
¿somos?, ¿estamos? |
| you are (you're) |
you are not (you're not) |
are you? |
| sois, estáis |
no sois, no estáis |
¿sois?, ¿estáis? |
| they are (they're) |
they are not (they're not) |
are they? |
| ellos son, están |
ellos no son, no están |
¿son, están ellos? |
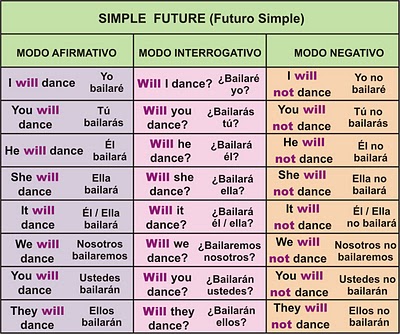
Simple Present
El Presente Simple es un tiempo verbal que se utiliza para describir acciones habituales que suceden con cierta frecuencia y no hace referencia a si está ocurriendo en el momento actual.I play tennis. Yo juego al tenis.
(Se refiere al trabajo que desarrolla una persona frecuentemente). They travel to Madrid. Ellos viajan a Madrid.(Habla de un viaje que se repite a diario, aunque el sujeto no lo esté realizando ahora).A continuación se muestran las formas afirmativa, interrogativa y negativa de este tiempo verbal:
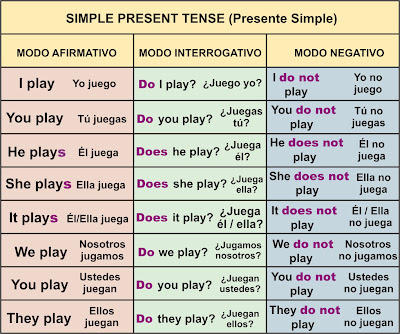
PRESENT CONTINUO
En el cuadro superior se utiliza el verbo jugar (TO PLAY) a modo de ejemplo.
Puede utilizarse además para referirse a situaciones que suceden alrededor del momento en el que se habla, aunque no precisamente tiene que ser en este mismo momento, por ejemplo:
He is working in a bank. Él está trabajando en un banco.
(Significa que es su trabajo habitual, aunque no necesariamente la persona debe estar trabajando ahora).
PERSONAL INFORMATION.
Names
What is your name?
My name is _______.
What is your surname / last name?
My surname / last name is _______.
Do you have a nickname?
Yes, my nickname is _______ or No, I don't.
Work & Occupation
What do you do?
I am a _______.
Where do you work?
I work at _______.
Do you like your job?
Yes, I do. or No, I don't.
Why do you like your job?
I like my job because _______.
MONTHS OF THE YEAR
<form action="https://www.idiomasgratis.com/ig_corregir.php?id_recurso=" 49"="" name="frmRecurso" style="font-family: tahoma, arial, sans-serif;">
January-Enero.
February-Febrero.
March-Marzo.
April-Abril.
May-Mayo.
June-Junio.
July-Julio.
August-Agosto.
September-Septiembre.
October-October.
November-Noviembre.
December-Diciembre.
DAYS OF THE WEEK
Monday-Lunes.
Tuesday-Martes.
Wednesday-Miércoles.
Thursday-Jueves.
Friday-Viernes.
Saturday-Sábado.
Sunday-Domingo
ORDINAL NUMBERS
Números ordinales
Cuando se colocan objetos en orden, se utilizan los números ordinales para nombrar su posición. Los números ordinales son similares a los números que has aprendido anteriormente (llamados números cardinales). Si diez alumnos corren una carrera, diríamos que el estudiante que corrió más rápido obtuvo el primer lugar, el próximo estudiante llegó en segundo lugar y así sucesivamente.
Los primeros diez números ordinales son:
-
Primero
-
Segundo
-
Tercero
-
Cuarto
-
Quinto
-
Sexto
-
Séptimo
-
Octavo
-
Noveno
-
Décimo

CARDINAL NUMBERS

GREETINGS AND FAREWELLS
|
Saludos en Ingles
|
Español
|
| Hello, Hi |
Hola |
| Good morning |
Buenos días |
| Good afternoon |
Buenas tardes |
| Good evening |
Buenas noches (Al llegar) |
| How are you doing? |
¿Como te va? |
| How are you getting on? |
¿Como andas? |
| How are things? |
¿Qué tal? |
| Nice / pleased to meet you. |
Encantado, Mucho gusto en conocerte |
| Nice to see you again. |
Encantado de verle de nuevo. |
|
Despedidas en Ingles
|
Español
|
| Goodbye / bye |
Hasta luego/Adios |
| See you soon |
Hasta pronto |
| See you tomorrow |
Hasta mañana |
| See you later |
Hasta luego |
| Good night |
Buenas noches (Al irse) |
| Take care |
Cuidate |
| Best wishes! |
Recuerdos / Mis mejores deseos |
| Good to have seen you again. |
Ha sido un placer verte de nuevo |
COUNTRIES AND NATIONALITIES
|
COUNTRY
|
NATIONALITY
|
 |
|
AFGHANISTAN
|
AFGHAN
|
afgánistan, áfgan
|
|
ALGERIA
|
ALGERIAN
|
alyíria, alyírian
|
|
ANDORRA
|
ANDORRAN
|
andórra, andórran
|
|
ARABIA
|
ARABIAN
|
arábia, arábian
|
|
ARGENTINA
|
ARGENTINIAN,
ARGENTINE
|
aryentína, aryentínian, aryentín
|
|
AUSTRALIA
|
AUSTRALIAN
|
ostréilia, austréilian
|
|
AUSTRIA
|
AUSTRIAN
|
óstria, óstrian
|
|
the BAHAMAS
|
BAHAMIAN
|
de bajámas, bajámian
|
|
BELGIUM
|
BELGIAN
|
bélyium, bélyian
|
|
BOLIVIA
|
BOLIVIAN
|
bolí:via, bolí:vian
|
|
BRAZIL
|
BRAZILIAN
|
bresíl, bresílian
|
|
BULGARIA
|
BULGARIAN
|
bulgária, bulgárian
|
|
CAMBODIA
|
CAMBODIAN
|
kambóudia, kambóudian
|
|
CANADA
|
CANADIAN
|
kánada, kanéidian
|
|
CHILE
|
CHILEAN
|
chíle, chiléan
|
|
CHINA
|
CHINESE
|
cháina, chainí:s
|
|
COLOMBIA
|
COLOMBIAN
|
kolómbia, kolómbian
|
|
COSTA RICA
|
COSTA RICAN
|
kásta-rí:ka, kásta-rí:kan
|
|
CUBA
|
CUBAN
|
kiúba, kiúban
|
|
CYPRUS
|
CYPRIOT
|
sáiprus, sípriot
|
|
CZECHOSLOVAKIA
|
CZECHOSLOSVAKIAN
|
shekoslovákia, shekoslovákian
|
|
DENMARK
|
DANISH
|
dénmark, dánish
|
|
the DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
|
DOMINICAN
|
de domínikan ripáblik, domínikan
|
|
ECUADOR
|
ECUADORIAN
|
ekuádo:r, ekuadórian
|
|
EGYPT
|
EGYPTIAN
|
íyipt, iyípshan
|
|
ENGLAND
|
ENGLISH
|
íngland, ínglish
|
|
EL SALVADOR
|
SALVADOREAN
|
el salvadó:r, salvadorí:an
|
DAILY ACTIVITIES AND ROUTINES

PHYSICAL APPEARANCE OR DESCRIPTION
- APPEARANCE: ASPECTO
- ATTRACTIVE: ATRACTIVO
- AVERAGE BUILD: DE CONSTITUCIÓN MEDIA
- BALD: CALVO
- BEARD: BARBA
- BEAUTIFUL: GUAPA, GUAPO
- BEAUTIFUL: HERMOSO
- BIRTHMARK: MARCA DE NACIMIENTO
- BLACK HAIR: CABELLO NEGRO
- BLOND, FAIR: RUBIO
- BLOND, FAIR HAIR: CABELLO RUBIO
- BRACES: APARATO DE ORTODONCIA
- BRAID: TRENZA
- BROWN HAIR: CABELLO CASTAÑO
- BURNED: QUEMADO
- CURLY HAIR: CABELLO RIZADO
- DARK: MORENO, OSCURO
- DARK HAIR: CABELLO OSCURO
- DISABLED: MINUSVALIDO, DESCAPACITADO
- ELEGANT, SMART: ELEGANTE
- FAT: GORDO
- FRECKLES: PECAS
- GOOD-LOOKING: GUAPO
- GREY HAIR: CABELLO CANOSO
- HAIR: PELO
- HANDSOME: GUAPO, (SOLO PARA HOMBRES)
- HANDSOME: APUESTO, GUAPO
- INTELLIGENT: INTELIGENTE
- LAME: COJO
- LIGHT HAIR: CABELLO CORTO.
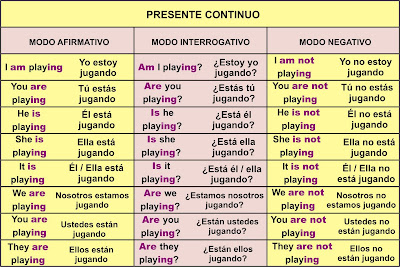
PRESENT PROGRESSIVE
Notes:
- The written lesson is below.
- Links to quizzes, tests, etc. are to the left.
The present progressive is formed by combining the verb "to be" with the present participle. (The present participle is merely the "-ing" form of a verb.)
I am studying.
I am studying with María.
In English, present progressive can be used to describe what is happening now, or what will happen in the future.
I am studying now.
I am studying with María tonight.
In Spanish, the present progressive is only used to describe an action that is in the process of taking place. It is not used for future actions.
I am studying now.
(use present progressive)
I am studying with María tonight.
(do not use present progressive)
To form the present progressive in Spanish, combine a form of "estar" with the present participle.
Estoy hablando.
I am speaking.
Juan está comiendo.
John is eating.
María está escribiendo una carta.
Mary is writing a letter.
In order to form the present progressive, you must know how to conjugate the verb estar, and how to form the present participle. You already know how to conjugate the verb estar:
estar
estoy
estás
está
estamos
estáis
están
To form the present participle of regular -ar verbs, add -ando to the stem of the verb.
hablar: hablando
(hablar - ar + ando)
trabajar: trabajando
(trabajar - ar + ando)
estudiar: estudiando
(estudiar - ar + ando)
To form the present participle of regular -er and -ir verbs, add -iendo to the stem of the verb.
comer: comiendo
(comer - er + iendo)
hacer: haciendo
(hacer - er + iendo)
vivir: viviendo
(vivir - ir + iendo)
escribir: escribiendo
(escribir - ir + iendo)
To form the present participle of -ir stem changing verbs, change e:i and o:u in the stem, and then add -iendo to the stem of the verb.
servir: sirviendo
pedir: pidiendo
decir: diciendo
dormir: durmiendo
morir: muriendo
poder: pudiendo
Sometimes when forming the present participle it is necessary to change the spelling of a word so that it agrees with the way it is pronounced. We call this an "orthographic" change. Here are some common examples:
caer: cayendo
creer: creyendo
huir: huyendo
ir: yendo
influir: influyendo
oír: oyendo
traer: trayendo
leer: leyendo
seguir: siguiendo
WH QUESTIONS